Insights into hydrogen bond donor promoted fixation of carbon dioxide with epoxides catalyzed by ionic liquids†
Abstract
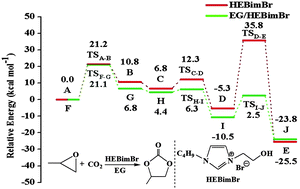
Catalytic coupling of carbon dioxide with epoxides to obtain cyclic carbonates is an important reaction that has been receiving renewed interest. In this contribution, the cycloaddition reaction in the presence of various hydrogen bond donors (HBDs) catalyzed by hydroxyl/carboxyl task-specific ionic liquids (ILs) is studied in detail. It was found that the activity of ILs could be significantly enhanced in the presence of ethylene glycol (EG), and EG/HEBimBr were the most efficient catalysts for the CO2 cycloaddition to propylene oxide. Moreover, the binary catalysts were also efficiently versatile for the CO2 cycloaddition to less active epoxides such as styrene oxide and cyclohexene oxide. Besides, the minimum energy paths for this hydrogen bond-promoted catalytic reaction were calculated using the density functional theory (DFT) method. The DFT results suggested that the ring-closing reaction was the rate-determining step in the HEBimBr-catalyzed cycloaddition reaction but the EG addition could remarkably reduce its energy barrier as the formation of a hydrogen bond between EG and the oxygen atom of epoxides led this process along the standard SN2 mechanism. As a result, the ring-opening reaction became the rate-determining step in the EG/HEBimBr-catalyzed cycloaddition reaction. The work reported herein helped the understanding and design of catalysts for efficient fixation of CO2 to epoxides via hydrogen bond activation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...