Abnormal thermal expansion properties of cubic NaZn13-type La(Fe,Al)13 compounds†
Abstract
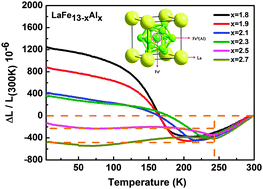
The cubic NaZn13-type La(Fe,Al)13 compounds were synthesized, and their linear thermal expansion properties were investigated in the temperature range of 4.2–300 K. It was found that these compounds exhibit abnormal thermal expansion behavior, i.e., pronounced negative thermal expansion (NTE) or zero thermal expansion (ZTE) behavior, below the Curie temperature due to the magnetovolume effect (MVE). Moreover, in the La(Fe,Al)13 compounds, the modification of the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) as well as the abnormal thermal expansion (ATE) temperature-window is achieved through optimizing the proportion of Fe and Al. Typically, the average CTE of the LaFe13−xAlx compounds with x = 1.8 reaches as large as −10.47 × 10−6 K−1 between 100 and 225 K (ΔT = 125 K). Also, the ZTE temperature-window of the LaFe13−xAlx compounds with x = 2.5 and x = 2.7 could be broadened to 245 K (from 5 to 250 K). Besides, the magnetic properties of these compounds were measured and correlated with the abnormal thermal expansion behavior. The present results highlight the potential application of such La(Fe,Al)13 compounds with abnormal thermal expansion properties in cryogenic engineering.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...