Ab initio quantum dynamical analysis of ultrafast nonradiative transitions via conical intersections in pyrazine
Abstract
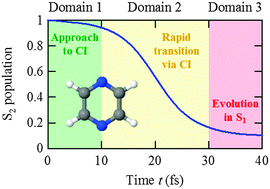
We theoretically investigated the mechanism of ultrafast nonradiative transition through conical intersections in photoexcited pyrazine by ab initio quantum dynamical calculations. This work was motivated by the recent theoretical and experimental studies that presented conflicting results: the former is the on-the-fly semiclassical surface hopping calculation combined with the time-dependent density functional theory, which showed that nonadiabatic transitions from the optically bright S2 (1B2u, ππ*) state to the optically dark S3 (1Au, nπ*) and S4 (1B2g, nπ*) states take place predominantly at the initial stage of electronic relaxation [U. Werner et al., Chem. Phys., 2008, 349, 319]; the latter is the pump–probe photoelectron spectroscopic measurement, which reported the S2 lifetime (22 ± 3 fs) of nonradiative decay to the almost dark S1 (1B3u, nπ*) state [Y.-I. Suzuki et al., J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 132, 174302]. We constructed adiabatic and diabatic potential energy surfaces of these ππ* and nπ* states using the multireference configuration interaction method and calculated their diabatic couplings within two-dimensional subspaces spanned by selected ground-state normal coordinates. Contrary to the surface hopping study, our nuclear wave packet simulations demonstrated that nonadiabatic transitions to the S3 and S4 states are so small that the conventional two-state (S1 and S2) picture is valid. Ultrafast internal conversion of pyrazine, which is deemed to proceed with a 22 fs lifetime, in fact consists of three consecutive steps: (i) the wave packet excited to the S2 state travels toward the S2–S1 conical intersection in 10 fs, (ii) the nonadiabatic transition to the S1 state progresses at a rapid rate corresponding to a transient lifetime of 7 fs, and (iii) intramolecular vibrational energy redistribution occurs in the S1 state in about 80 fs after optical excitation. To verify this prediction, time-resolved experiments with a resolution of several fs or shorter are desirable.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...