Nanostructure of mixtures of protic ionic liquids and lithium salts: effect of alkyl chain length
Abstract
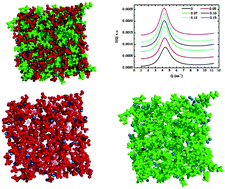
The bulk structure of mixtures of two protic ionic liquids, propylammonium nitrate and butylammonium nitrate, with a salt with a common anion, is analyzed at room temperature by means of small angle X-ray scattering and classical molecular dynamics simulations. The study of several structural properties, such as density, radial distribution functions, spatial distribution functions, hydrogen bonds, coordination numbers and velocity autocorrelation functions, demonstrates that increasing the alkyl chain length of the alkylammonium cation results in more segregated, better defined polar and apolar domains, the latter having a larger size. This increase, ascribed to the erosion of the H-bond network in the ionic liquid polar regions as salt is added, is confirmed by means of small angle X-ray scattering measurements, which show a clear linear increase of the characteristic spatial sizes of the studied protic ionic liquids with salt concentration, similar to that previously reported for ethylammonium nitrate (J. Phys. Chem. B, 2014, 118, 761–770). In addition, larger ionic liquid cations lead to a lower degree of hydrogen bonding and to more sparsely packed three-dimensional structures, which are more easily perturbed by the addition of lithium salts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...