Origin of ion selectivity at the air/water interface†
Abstract
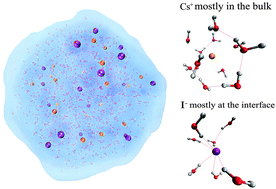
Among many characteristics of ions, their capability to accumulate at air/water interfaces is a particular issue that has been the subject of much research attention. For example, the accumulation of halide anions (Cl−, Br−, I−) at the water surface is of great importance to heterogeneous reactions that are of environmental concern. However, the actual mechanism that drives anions towards the air/water interface remains unclear. In this work, we have performed atomistic simulations using polarizable models to mimic ionic behavior under atmospheric conditions. We find that larger anions are abundant at the water surface and that the cations are pulled closer to the surface by the counterions. We propose that polarization effects stabilize the anions with large radii when approaching the surface. This energetically more favorable situation is caused by the fact that the more polarized anions at the surface attract water molecules more strongly. Of relevance is also the ordering of the surface water molecules with their hydrogen atoms pointing outwards which induce an external electronic field that leads to a different surface behavior of anions and cations. The water–water interaction is weakened by the distinct water–ion attraction, a point contradicting the proposition that F− is a kosmotrope. The simulation results thus allow us to obtain a more holistic understanding of the interfacial properties of ionic solutions and atmospheric aerosols.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...