Excited-state proton coupled electron transfer between photolyase and the damaged DNA through water wire: a photo-repair mechanism†
Abstract
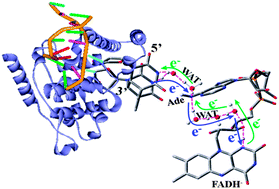
The photolyase enzyme absorbs blue light to repair damaged DNA through a cyclic electron transfer reaction. A description of the underlying mechanism has proven to be a challenging issue for both experimental and theoretical studies. In the present work, combined CASPT2//CASSCF/AMBER (QM/MM) calculations have been performed for damaged DNA in photolyase. A proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) mechanism has been determined for restoring cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD) to two normal thymine bases by irradiation of photolyase. A well-defined water wire between FADH− and CPD was determined as a bridge to assist the PCET process within FADH− and thereby trigger the forward electron transfer to CPD. The subsequent CPD splitting and the alternation of the H-bond pattern proceed in a concerted way, which makes the productive backward electron transfer occur on an ultrafast timescale. A local minimum of SCT(1ππ*)-LMin was identified on the pathway of the futile backward electron transfer (BET), which is stabilized by the strong H-bond interaction between the water wire and CPD. As a result, the futile BET process is endothermic by ∼18.0 kcal mol−1, which is responsible for a 2.4 ns timescale inferred experimentally for the futile BET process. Besides the unbiased interpretation for the majority of the experimental findings, the present study provides a new excited-state PCET mechanism, which leads to a significant step toward a deeper understanding of the photo-repair process of damaged-DNA by the photolyase enzyme.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...