Photoinduced desorption of CO from rutile TiO2: elucidation of a new desorption mechanism using first principles
Abstract
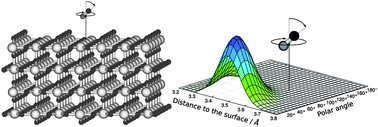
Due to its high photocatalytic activity, TiO2 is of eminent interest for a manifold of applications ranging from surface catalysis up to solar energy conversion. However, the fundamental mechanisms of the underlying surface photochemistry are by no means understood. Focussing on this drawback, laser-induced photodesorption of CO on an ideal rutile TiO2(110) surface is studied using first principles in terms of a model system. This paper presents both quantum chemical as well as quantum dynamical results, taking into account the desorption coordinate Z, the polar angle θ, and the azimuth angle ϕ of the adsorbate. Detailed insight into the fundamental mechanisms of the photodesorption process in this model system is obtained, and a new desorption scenario is elucidated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...