Ag nanoparticles–anchored reduced graphene oxide catalyst for oxygen electrode reaction in aqueous electrolytes and also a non-aqueous electrolyte for Li–O2 cells†
Abstract
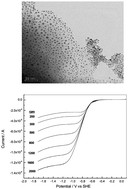
Silver nanoparticles–anchored reduced graphene oxide (Ag–RGO) is prepared by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and Ag+ ions in an aqueous medium by ethylene glycol as the reducing agent. Ag particles of average size of 4.7 nm were uniformly distributed on the RGO sheets. Oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is studied on Ag–RGO catalyst in both aqueous and non-aqueous electrolytes by using cyclic voltammetry and rotating disk electrode techniques. As the interest in non-aqueous electrolyte is to study the catalytic performance of Ag–RGO for rechargeable Li–O2 cells, these cells are assembled and characterized. Li–O2 cells with Ag–RGO as the oxygen electrode catalyst are subjected to charge–discharge cycling at several current densities. A discharge capacity of 11 950 mA h g−1 (11.29 mA h cm−2) is obtained initially at low current density. Although there is a decrease in the capacity on repeated discharge–charge cycling initially, a stable capacity is observed for about 30 cycles. The results indicate that Ag–RGO is a suitable catalyst for rechargeable Li–O2 cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...