Combinatorial effect of rolling and carbonaceous nanoparticles on the evolution of crystallographic texture and structural properties of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene
Abstract
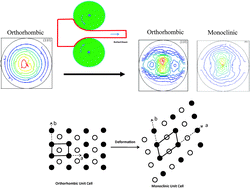
Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (PE) is a structural polymer widely used in biomedical implants. The mechanical properties of PE can be improved either by controlled crystalline orientation (texture) or by the addition of reinforcing agents. However, the combinatorial effect has not received much attention. The objective of this study was to characterize the structure and mechanical properties of PE composites incorporating multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and reduced graphene oxide (RGO) subjected to hot rolling. The wide angle X-ray diffraction studies revealed that mechanical deformation resulted in a mixture of orthorhombic and monoclinic crystals. Furthermore, the presence of nanoparticles resulted in lower crystallinity in PE with smaller crystallite size, more so in RGO than in MWCNT composites. Rolling strengthened the texture of both orthorhombic and the monoclinic phases in PE. Presence of RGO weakened the texture of both phases of PE after rolling whereas MWCNT only mildly weakened the texture. This resulted in a reduction in the elastic modulus of RGO composites whereas moduli of neat polymer and the MWCNT composite increased after rolling. This study provides new insight into the role of nanoparticles in texture evolution during polymer processing with implications for processing of structural polymer composites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...