The catalytic reactions in the Cu–Li–Mg–H high capacity hydrogen storage system
Abstract
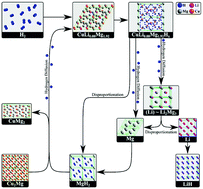
A family of hydrides, including the high capacity MgH2 and LiH, is reported. The disadvantages these hydrides normally display (high absorption/desorption temperatures and poor kinetics) are mitigated by Cu-hydride catalysis. This paper reports on the synthesis of novel CuLi0.08Mg1.42H4 and CuLi0.08Mg1.92H5 hydrides, which are structurally and thermodynamically characterized for the first time. The CuLi0.08Mg1.42H4 hydride structure in nanotubes is able to hold molecular H2, increasing the gravimetric and volumetric capacity of this compound. The catalytic effect these compounds show on hydride formation and decomposition of CuMg2 and Cu2Mg/MgH2, Li and LiH, Mg and MgH2 is analyzed. The Gibbs energy, decomposition temperature, and gravimetric capacity of the reactions occurring within the Cu–Li–Mg–H system are presented for the first time. First principles and phonon calculations are compared with experiments, including neutron spectroscopy. It is demonstrated that the most advantageous sample contains CuLi0.08Mg1.92 and (Li) ∼ Li2Mg3; it desorbs/absorbs hydrogen according to the reaction, 2CuLi0.08Mg1.42H4 + 2Li + 4MgH2 ↔ 2CuLi0.08Mg1.92 + Li2Mg3 + 8H2 at 114 °C (5.0 wt%) – 1 atm, falling within the proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications window. Finally the reaction 2CuLi0.08Mg1.42H4 + MgH2 ↔ 2CuLi0.08Mg1.92 + 5H2 at 15 °C (4.4 wt%) – 1 atm is found to be the main reaction of the samples containing CuLi0.08Mg1.92 that were analyzed in this study.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...