Intramolecular pnicogen interactions in phosphorus and arsenic analogues of proton sponges†
Abstract
A computational study of the intramolecular pnicogen bond in 1,8-bis-substituted naphthalene derivatives (ZXH and ZX2 with Z = P, As and X = H, F, Cl, and Br), structurally related to proton sponges, has been carried out. The aim of this paper is the study of their structural parameters, interaction energies and electronic properties such as electron density on the intramolecular interaction. The calculated geometrical parameters associated to the P⋯P interaction are in reasonably good agreement with the crystal structures found in a CSD search, in particular those of the halogen derivatives. Isodesmic reactions where the 1,8-bis-substituted derivatives are compared to monosubstituted derivatives have been calculated, indicating that the 1,8 derivatives are more stable than the monosubstituted ones for those cases with X–Z⋯Z–X and F–Z⋯Z–H alignments. Electron densities and Laplacians at the BCP on the pnicogen interactions suggest that they can be classified as pure closed shell interactions with a partial covalent character. Electron density shift maps are consistent with the results for intermolecular pnicogen interactions. Relationships between interatomic distance and electron density at the bond critical points and between interatomic distance and the orbital charge transfer stabilization energies have been found.
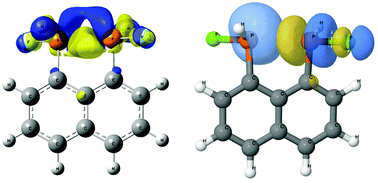

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...