Correlation of intercalation potential with d-electron configurations for cathode compounds of lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
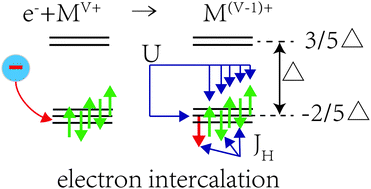
The d-electron localization is widely recognized as important to transport properties of transition metal compounds, but its role in the energy conversion of intercalation reactions of cathode compounds is still not fully explored. In this work, the correlation of intercalation potential with electron affinity, a key energy term controlling electron intercalation, then with d-electron configuration, is investigated. Firstly, we find that the change of the intercalation potential with respect to the transition metal cations within the same structure class is correlated in an approximately mirror relationship with the electron affinity, based on first-principles calculations on three typical categories of cathode compounds including layered oxides and polyoxyanions Then, by using a new model Hamiltonian based on the crystal-field theory, we reveal that the evolution is governed by the combination of the crystal-field splitting and the on-site d–d exchange interactions. Further, we show that the charge order in solid-solution composites and the compatibility of multi-electron redox steps could be inferred from the energy terms with the d-electron configuration alternations. These findings may be applied to rationally designing new chemistry for the lithium-ion batteries and other metal-ion batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...