Separating the redox couple for highly efficient solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
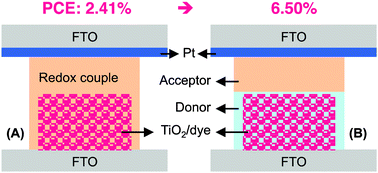
To minimize the charge recombination between electrons and the electron acceptor in solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells, we propose a separated electron donor and acceptor of a redox couple in the photoanode and in the cathode, respectively. Owing to the absence of the acceptor in the photoanode initially, the charge recombination rate is retarded remarkably, resulting in an increase of the short-circuit photocurrent by >2-fold, open-circuit photovoltage by 71 mV and power conversion efficiency by >2.5-fold.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...