Size-selected gold clusters on porous titania as the most “gold-efficient” heterogeneous catalysts
Abstract
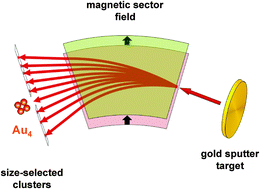
Research on homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis is indeed convergent and finds subnanometric particles to be at the heart of catalytically active species. Here, monodisperse gold clusters are deposited from the gas phase onto porous titania generating well-defined model systems and the resulting composite materials exhibit a sharp size-dependency on the number of gold atoms per cluster and exceptionally high-turnovers toward the bromination of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene are observed. This indicates that the deliberate generation of active centres is of utmost importance for the creation of the most “gold-efficient” catalysts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...