Carbon dioxide reduction via light activation of a ruthenium–Ni(cyclam) complex†
Abstract
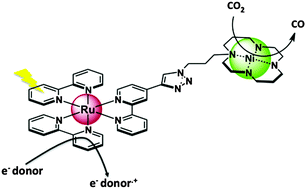
In this paper we report the synthesis of a chromophore–catalyst assembly designed for the photoreduction of carbon dioxide. The chromophore unit is made up of a ruthenium trisbipyridyl-like unit covalently attached to a nickel cyclam (cyclam = 1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane) via a triazole ring. The intramolecular electron transfer activation of the catalyst unit by visible light was studied by nanosecond flash photolysis and EPR spectroscopy. In aqueous solutions (pH = 6.5), activation of the RuII–NiII modular assembly with 450 nm visible light in the presence of a sacrificial electron donor accomplishes the reduction of CO2 into CO and H2 in a ratio of 2.7 to 1.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Photosynthesis: From Natural to Artificial

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...