Does the tautomeric status of the adenine bases change upon the dissociation of the A*·Asyn Topal–Fresco DNA mismatch? A combined QM and QTAIM atomistic insight†
Abstract
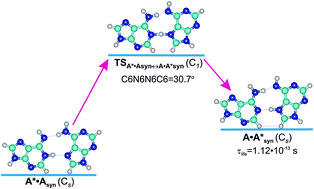
We have scrupulously explored the tautomerisation mechanism via the double proton transfer of the A*·Asyn Topal–Fresco base mispair (Cs symmetry), formed by the imino and amino tautomers of the adenine DNA base in the anti- and syn-conformations, respectively, bridging quantum-mechanical calculations with Bader's quantum theory of atoms in molecules. It was found that the A*·Asyn ↔ A·A*syn tautomerisation is the asynchronous concerted process. It was established that the A*·Asyn DNA mismatch is stabilized by the N6H⋯N6 (6.35) and N1H⋯N7 (6.17) hydrogen (H) bonds, whereas the A·A*syn base mispair (Cs) by the N6H⋯N6 (8.82) and N7H⋯N1 (9.78) H-bonds and the C8H⋯HC2 HH-bond (0.30 kcal mol−1). Using the sweeps of the energies of the intermolecular H-bonds, it was observed that the N6H⋯N6 and N1H⋯N7/N7H⋯N1 H-bonds are anti-cooperative and mutually weaken each other in the A*·Asyn and A·A*syn mispairs. It was revealed that the A·A*syn DNA mismatch is a dynamically unstable structure with a short lifetime of 1.12 × 10−13 s and any of its 6 low-frequency intermolecular vibrations can develop during this period of time. This observation makes it impossible to change the tautomeric status of the A bases upon the dissociation of the A*·Asyn base mispair into the monomers during DNA replication.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...