Weak hydrogen bonding motifs of ethylamino neurotransmitter radical cations in a hydrophobic environment: infrared spectra of tryptamine+–(N2)n clusters (n ≤ 6)
Abstract
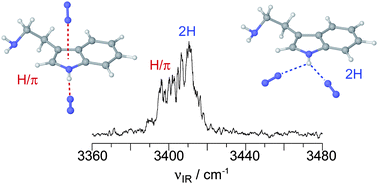
Size-selected clusters of the tryptamine cation with N2 ligands, TRA+–(N2)n with n = 1–6, are investigated by infrared photodissociation (IRPD) spectroscopy in the hydride stretch range and quantum chemical calculations at the ωB97X-D/cc-pVTZ level to characterize the microsolvation of this prototypical aromatic ethylamino neurotransmitter radical cation in a nonpolar solvent. Two types of structural isomers exhibiting different interaction motifs are identified for the TRA+–N2 dimer, namely the TRA+–N2(H) global minimum, in which N2 forms a linear hydrogen bond (H-bond) to the indolic NH group, and the less stable TRA+–N2(π) local minima, in which N2 binds to the aromatic π electron system of the indolic pyrrole ring. The IRPD spectrum of TRA+–(N2)2 is consistent with contributions from two structural H-bound isomers with similar calculated stabilization energies. The first isomer, denoted as TRA+–(N2)2(2H), exhibits an asymmetric bifurcated planar H-bonding motif, in which both N2 ligands are attached to the indolic NH group in the aromatic plane via H-bonding and charge–quadrupole interactions. The second isomer, denoted as TRA+–(N2)2(H/π), has a single and nearly linear H-bond of the first N2 ligand to the indolic NH group, whereas the second ligand is π-bonded to the pyrrole ring. The natural bond orbital analysis of TRA+–(N2)2 reveals that the total stability of these types of clusters is not only controlled by the local H-bond strengths between the indolic NH group and the N2 ligands but also by a subtle balance between various contributing intermolecular interactions, including local H-bonds, charge–quadrupole and induction interactions, dispersion, and exchange repulsion. The systematic spectral shifts as a function of cluster size suggest that the larger TRA+–(N2)n clusters with n = 3–6 are composed of the strongly bound TRA+–(N2)2(2H) core ion to which further N2 ligands are weakly attached to either the π electron system or the indolic NH proton by stacking and charge–quadrupole forces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...