Imaging the photodissociation dynamics of neutral metal clusters: copper dimer, Cu2, and copper oxide, CuO
Abstract
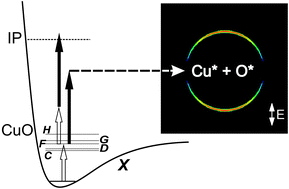
The spectroscopy and UV photodissociation dynamics of Cu2 and CuO have been studied using a combination of one- and two-colour excitation and velocity map imaging. Resonant excitation of Cu2via the J ← X 1Σg+ transition leads to significant fragmentation which is interpreted in terms of a combination of direct dissociation of Cu2+ 2Π produced in the resonant two-photon ionization process and dissociation of excited Cu2 states above the ionization threshold. By fitting of the kinetic energy release spectra obtained from the velocity map images, we determine a value for the dissociation energy of the cation of D0 (Cu2+, X 2Σg+) of 1.713 ± 0.025 eV, which, when combined with known ionization energies, yields D0 (Cu2, X 1Σg+) = 1.886 ± 0.026 eV. In other experiments, resonant two colour (1 + 1′) excitation of CuO via a range of excited states (C, D, F, H), yields unusually simple VMI images indicating fragmentation into a single dissociation channel which has been identified as Cu* 2D3/2 + O* 1D. Taken together, this data gives a CuO bond dissociation energy of 3.041 ± 0.030 eV. Finally, the production of Cu2+ with kinetic energy = 705 ± 75 cm−1 is tentatively interpreted as photolysis of Cu3 yielding Cu* + Cu2 X 1Σg+ from which a dissociation energy of Cu3 of 0.605 ± 0.030 eV is deduced.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Imaging molecular dynamics

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...