Formation of supported rhodium clusters from mononuclear rhodium complexes controlled by the support and ligands on rhodium†
Abstract
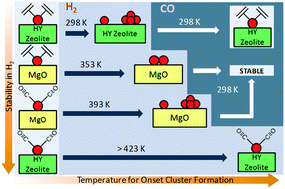
Extremely small supported rhodium clusters were prepared from rhodium complexes on the surfaces of solids with contrasting electron-donor properties. The samples were characterized by infrared and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopies to determine the changes occurring in the rhodium species resulting from treatments in hydrogen. Rhodium cluster formation occurred in the presence of H2, and the first steps are controlled by the electron-donor properties of the support—which acts as a ligand—and the other ligands bonded to the rhodium. The cluster formation begins at a lower temperature when the support is zeolite HY than when it is the better electron-donor MgO, provided that the other ligands on rhodium are ethene. In contrast, when these other ligands are CO, the pattern is reversed. The choice of ligands including the support also allows regulation of the stoichiometry of the surface transformations in H2 and the stability of the structures formed in the presence of other reactants. The combination of MgO as the support and ethene as a ligand allows restriction of the rhodium cluster size to the smallest possible—and these were formed in high yields. The data presented here are among the first characterizing the first steps of metal cluster formation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...