On the correlation between dye coverage and photoelectrochemical performance in dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
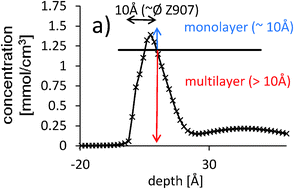
Concentration depth profiles of the ruthenium based dyes Z907 and N719 adsorbed onto titania are measured directly and used for determining the adsorption isotherm of the dyes. Dye layers formed by both grow in islands on the titania which do not cover the entire titania surface even at the maximum coverage. Impedance spectroscopy in conjunction with the adsorption isotherms shows that recombination losses mainly appear between the dye and the electrolyte solution. The short circuit current and the efficiency increase linearly with the dye coverage. The open circuit voltage slightly increases with increasing dye coverage which is interpreted as most likely to be a consequence of the higher charge in the particles upon higher dye loading on the TiO2 surface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...