Optical near-field excitation at commercial scanning probe microscopy tips: a theoretical and experimental investigation
Abstract
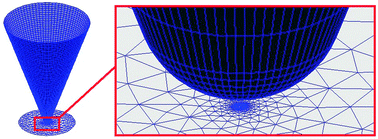
A systematic study of the influence of the excitation angle, the light polarization and the coating thickness of commercial SPM tips on the field enhancement in an apertureless scanning near-field optical microscope is presented. A new method to optimize the alignment of the electric field vector along the major tip axis by measuring the resonance frequency was developed. The simulations were performed with a MNPBEM toolbox based on the Boundary Element Method (BEM). The influence of the coating thickness was investigated for the first time. Coatings below 40 nm showed a drastic influence both on the resonance wavelength and the enhancement. A shift to higher angles of incidence for the maximum enhancement could be observed for greater tip radii.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...