The relative roles of electrostatics and dispersion in the stabilization of halogen bonds
Abstract
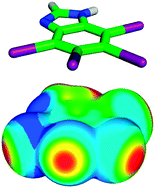
In this work we highlight recent work aimed at the characterization of halogen bonds. Here we discuss the origins of the σ-hole, the modulation of halogen bond strength by changing of neighboring chemical groups (i.e. halogen bond tuning), the performance of various computational methods in treating halogen bonds, and the strength and character of the halogen bond, the dihalogen bond, and two hydrogen bonds in bromomethanol dimers (which serve as model complexes) are compared. Symmetry adapted perturbation theory analysis of halogen bonding complexes indicates that halogen bonds strongly depend on both dispersion and electrostatics. The electrostatic interaction that occurs between the halogen σ-hole and the electronegative halogen bond donor is responsible for the high degree of directionality exhibited by halogen bonds. Because these noncovalent interactions have a strong dispersion component, it is important that the computational method used to treat a halogen bonding system be chosen very carefully, with correlated methods (such as CCSD(T)) being optimal. It is also noted here that most forcefield-based molecular mechanics methods do not describe the halogen σ-hole, and thus are not suitable for treating systems with halogen bonds. Recent attempts to improve the molecular mechanics description of halogen bonds are also discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...