Reducing the spin–spin interaction of stable carbon radicals
Abstract
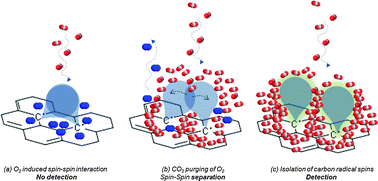
We report the discovery that a flow of CO2, N2 or He can sufficiently reduce the spin–spin interactions of specific stable carbon centered radicals by displacing the molecular oxygen in the atmosphere enabling their detection via electron paramagnetic resonance (
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...