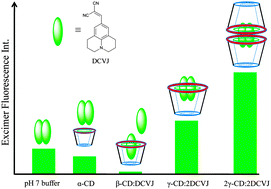
This article reports the alteration of the excited state photophysics of a molecular rotor, namely 9-(dicyano-vinyl)julolidine (DCVJ), which has been extensively used to report protein aggregation and protein conformational changes, by the various cavity sizes of cyclodextrin (CD) macrocyclic hosts, with the help of steady state, time-resolved fluorescence techniques. It is observed that, in the presence of α-CD, the characteristic features of both the monomer and excimer emissions of DCVJ are almost unperturbed. However, in the presence of β-CD, the excited photophysics of the molecule is significantly perturbed, and it is noted that β-CD inhibits the excimer formation drift of DCVJ by incorporation of a DCVJ monomer inside its cavity. The most striking findings are observed in the case of γ-CD. Initially, the excimer peak intensity drops and the monomer intensity increases, due to the 1 : 1 DCVJ/γ-CD inclusion complex formation. Above a certain concentration, another DCVJ molecule is accommodated inside the γ-CD cavity and forms an excimer, which is reflected in the intensification of the excimer peak. At higher γ-CD concentration the fluorescence intensity of the excimer shoots up, due to the formation of 2 : 2 host–guest complex, in which an additional γ-CD molecule provides extra stabilization to the excimer. Insight on the molecular picture of this host–guest interaction has been provided by docking studies followed by quantum chemical calculations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...