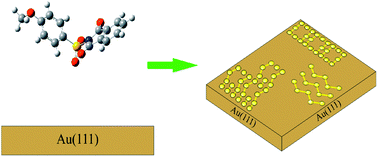
We report on a series of arene sulfonyl phthalimides which were prepared and used to modify polycrystalline gold and Au(111) gold surfaces. Three investigated compounds are the p-iodo-, the p-methoxy-, and the p-fluoro-benzenesulfonyl phthalimides. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), cyclic voltammetry (CV), and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) studies were used to characterize the modified surfaces. The XPS data show that all three investigated compounds decompose on gold surfaces. The decomposition leads to the adsorption of sulfur and ejection of the other groups except for the p-iodo compound, which also leads to the deposition of iodine. The cyclic voltammetry data confirm these results and show that high coverage values of deposited sulfur are obtained. High-resolution STM imaging showed a dynamic behaviour of sulfur on gold for all compounds. Movement of sulfur species on the Au(111) surface is observed. Various phases including a new ‘zig-zag’ pattern and a new 2 : 1 line pattern are presented. Sequential STM imaging also showed movement of one area of sulfur while another remains static. These results are important because (i) they provide direct experimental evidence that these hexavalent sulfur compounds react with gold surfaces breaking all sulfur chemical bonds, (ii) they show that sulfonyl phthalimides can be used as efficient precursors for the deposition of sulfur on gold, and (iii) very importantly they show the adlayer nature of the sulfur modified gold surface which has been a heavily debated question.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...