New insights into the mechanism of electron transfer within flavohemoglobins: tunnelling pathways, packing density, thermodynamic and kinetic analyses†
Abstract
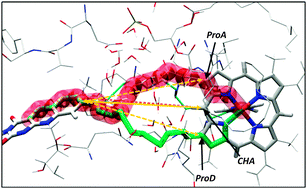
Flavohemoglobins (FlavoHb) are metalloenzymes catalyzing the reaction of nitric oxide dioxygenation. The
- This article is part of the themed collection: Electron Transfer Theory

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...