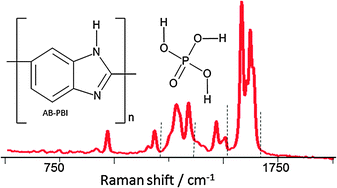
Poly(2,5-benzimidazole) (AB-PBI) membranes are investigated by studying the FT-Raman signals due to the benzimidazole ring vibration together with the C–C and C–H out-of- and in-plane ring deformations. By immersion in aqueous ortho-phosphoric acid for different time periods, membranes with various doping degrees, i.e. different molar fractions of acid, are prepared. The chemical–physical interactions between polymer and acid are studied through band shifting and intensity change of diagnostic peaks in the 500–2000 cm−1 spectral range. The formation of hydrogen bonding networks surrounding the polymer seems to be the main reason for the observed interactions. Only if the AB-PBI polymer is highly doped, the Raman spectra show an additional signal, which can be attributed to the presence of free phosphoric acid molecules in the polymer network. For low and intermediate doping degrees no evidence for free phosphoric acid molecules can be seen in the spectra. The extent of the polymer–phosphoric acid interactions in the doped membrane material is reinvestigated after a period of one month and the stability discussed. Our results provide insight into the role of phosphoric acid as a medium in the conductivity mechanism in polybenzimidazole.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...