An enthalpic approach to delineate the interactions of cations of imidazolium-based ionic liquids with molecular solvents†
Abstract
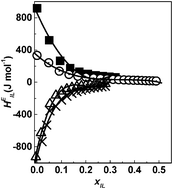
We present a systematic investigation on the enthalpic assessment of the interactions operating between the cation and anion of four imidazolium ionic liquids with aqueous and various nonaqueous solvents. Accurate experimental information gathered with the help of an isothermal titration calorimeter at 298.15 K has been analyzed for excess partial molar enthalpy of the ionic liquid, HEIL, in terms of hydrophobic and solvation effects. The variations in the limiting excess partial molar enthalpy of the ionic liquid, HE,∞IL, have been correlated with solvent properties. We have quantified the enthalpic effects due to dissociation of ionic liquids in very dilute solutions and to clathrate formation with the increasing concentration of ionic liquid. A change in enthalpic behavior from endothermic to exothermic is observed on increasing the carbon chain length attached to the imidazolium ring. The solvent reorganization around the cationic species has been unraveled by employing the ionic liquid interaction parameters called as HEIL–IL deduced from the HEIL data. The apparent relative molar enthalpy, φL, derived from HEIL data has been examined in the light of the specific ion interaction theory as advanced by Pitzer with accurate results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...