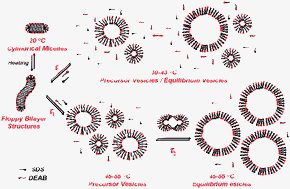
The kinetics of thermo-induced micelle-to-vesicle transitions in a catanionic surfactant system consisting of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and dodecyltriethylammonium bromide (DEAB) were investigated by the stopped-flow temperature jump technique, which can achieve T-jumps within ∼2–3 ms. SDS/DEAB aqueous mixtures ([SDS]/[DEAB] = 2/1, 10 mM) undergo microstructural transitions from cylindrical micelles to vesicles when heated above 33 °C. Upon T-jumps from 20 °C to final temperatures in the range of 25–31 °C, relaxation processes associated with negative amplitudes can be ascribed to the dilution-induced structural rearrangement of cylindrical micelles and to the dissolution of non-equilibrium mixed aggregates. In the final temperature range of 33–43 °C the obtained dynamic traces can be fitted by single exponential functions, revealing one relaxation time (τ) in the range of 82–440 s, which decreases with increasing temperature. This may be ascribed to the transformation of floppy bilayer structures into precursor vesicles followed by further growth into final equilibrium vesiclesvia the exchange and insertion/expulsion of surfactant monomers. In the final temperature range of 45–55 °C, vesicles are predominant. Here T-jump relaxations revealed a distinctly different kinetic behavior. All dynamic traces can only be fitted with double exponential functions, yielding two relaxation times (τ1 and τ2), exhibiting a considerable decrease with increasing final temperatures. The fast process (τ1 ∼ 5.2–28.5 s) should be assigned to the formation of non-equilibrium precursor vesicles, and the slow process (τ2 ∼ 188–694 s) should be ascribed to their further growth into final equilibrium vesiclesvia the fusion/fission of precursor vesicles. In contrast, the reverse vesicle-to-micelle transition process induced by a negative T-jump from elevated temperatures to 20 °C occurs quite fast and almost completes within the stopped-flow dead time (∼2–3 ms).
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...