Ion-specific weak adsorption of salts and water/octanol transfer free energy of a model amphiphilic hexapeptide†
Abstract
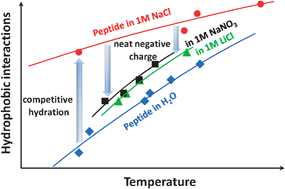
An amphiphilic hexapeptide has been used as a model to quantify how specific ion effects induced by addition of four salts tune the hydrophilic/hydrophobic balance and induce temperature-dependant coacervate formation from aqueous solution. The hexapeptide chosen is present as a dimer with low transfer energy from

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...