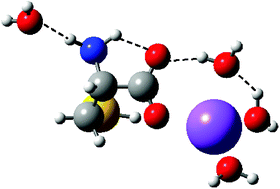
Absolute bond dissociation energies of water to sodium cysteine (Cys) cations and cysteine to hydrated sodium cations are determined experimentally by collision-induced dissociation of Na+Cys(H2O)x, where x = 1–4, complexes with xenon in a guided ion beam mass spectrometer. Experimental results show that the binding energies of water and cysteine to the complexes decrease monotonically with increasing number of water molecules. Quantum chemical calculations at three different levels show reasonable agreement with the experimental bond energies. The calculations indicate that the primary binding site for Na+ changes from charge-solvated tridentate chelation at the amino nitrogen, carbonyl oxygen, and sulfur side-chain for x = 0 and 1 to the C terminus of zwitterionic cysteine for x = 4, whereas different levels of theory provide conflicting predictions for x = 2 and 3. The first solvent shell of Na+Cys is found to be complete at four waters. This is fewer than needed for the aliphatic amino acid glycine, because the functionalized side-chain of Cys provides an internal solvation site, a binding motif that probably applies for most other functionalized amino acids.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...