Controlled full adder–subtractor by vibrational computing
Abstract
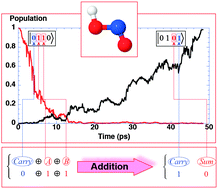
The implementation of a quantum-controlled full adder–subtractor of two binary digits and of a “carry in” or a “borrow in” is simulated by encoding four qubits in the vibrational eigenstates of a tetra-atomic molecule (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...