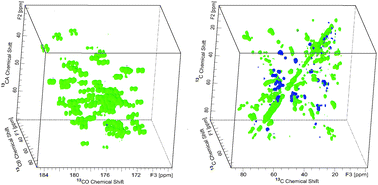
Scalar-based three-dimensional homonuclear correlation experiments are reported for 13C sidechain correlation in solid-state proteins. These experiments are based on a sensitive constant-time format, in which homonuclear scalar couplings are utilized for polarization transfer, but decoupled during chemical shift evolution, to yield highly resolved indirect dimensions and band selectivity as desired. The methods therefore yield spectra of high quality that give unique sets of sidechain correlations for small proteins even at 9.4 Tesla (400 MHz 1H frequency). We demonstrate versions of the pulse sequence that enable correlation from the sidechain to the backbone carbonyl as well as purely sidechain correlation sets; together these two data sets provide the majority of 13C–13C correlations for assignment. The polarization transfer efficiency is approximately 30% over two bonds. In the protein GB1 (56 residues), we find essentially all cross peaks uniquely resolved. We find similar efficiency of transfer (∼30%) in the 140 kDa tryptophan synthase (TS), since the relaxation rates of immobilized solid proteins are not sensitive to global molecular tumbling, as long as the correlation time is much longer than the magic-angle spinning rotor period. In 3D data sets of TS at 400 MHz, some peaks are resolved and, in combination with higher field data sets, we anticipate that assignments will be possible; in this vein, we demonstrate 2D 13C–13C spectra of TS at 900 MHz that are well resolved. These results together provide optimism about the prospects for assigning the spectra of such large enzymes in the solid state.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...