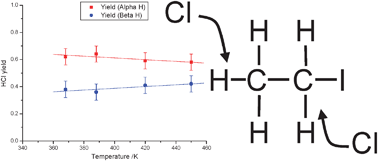
The reaction of chlorine atoms with alkyl iodides can play a role in the chemistry of the marine boundary layer. Previous studies have shown that at room temperature the reaction takes place via a complex mechanism including adduct formation. For the Cl + ethyl iodide reaction results on the thermodynamics of adduct formation and on the product yields are inconsistent. The kinetics of the reaction Cl + C2H5I have been studied by the direct observation of the HCl product in real time flash photolysis/IR absorption experiments as a function of temperature from 273 to 450 K. At temperatures above 375 K kinetic measurements confirm a direct process and the rate coefficient determined (4.85 ± 0.55) × 10−11 exp((−363 ± 51)/T) cm3 molecule−1 s−1 is in good agreement with previous direct determinations. Product yield studies have also been undertaken by comparing the HCl signal from Cl + C2H5I with that from a calibration reaction which shows that HCl is the sole product of the reaction at these temperatures. Yield studies with selectively deuterated ethyl iodide demonstrate that abstraction occurs predominantly from the α site, with the selectivity decreasing with temperature. Extrapolation of the yield data to 298 K predicts an α : β ratio of 0.68 : 0.32. At temperatures between 273 and 325 K a biexponential growth was observed for the HCl signal consistent with adduct formation. Analysis of the HCl time profiles allowed the extractions of the forward and reverse rate coefficients for adduct formation and hence the calculations of the thermodynamic properties of adduct formation. A third law analysis yields a value of ΔrH = (−54 ± 4) kJ mol−1. The value of ΔrH is in good agreement with a previous third law determination (J. J. Orlando, C. A. Piety, J. M. Nicovich, M. L. McKee, P. H. Wine, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2005, 109, 6659).
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...