Microhydration of guanine⋯cytosine base pairs, a theoretical Study on the role of water in stability, structure and tautomeric equilibrium†
Abstract
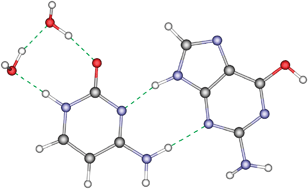
The potential energy surfaces of guanine⋯cytosine complexes and microhydrated guanine⋯cytosine (one and two

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...