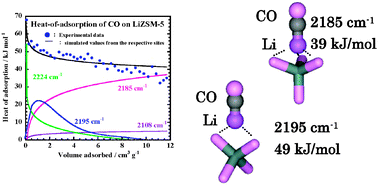
For alkali-metal ion-exchanged ZSM-5 zeolites (MZSM-5; M: Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) the analysis of ion-exchangeable sites was performed by means of a combined method based on IR spectroscopic and calorimetric measurements using CO as the probe molecule. The heat of adsorption of CO was found to be correlated with an IR frequency of stretching vibration of C–O in the adsorbed species. It was revealed that there exists at least two types of sites capable of ion-exchanging; for the lithium ion-exchanged ZSM-5 (LiZSM-5) CO adsorption on each type of site is evaluated to give a set of IR bands and heats of adsorption, 2195 cm−1 and 49 kJ mol−1, 2185 cm−1 and 39 kJ mol−1 with the aid of the newly developed method utilizing the data obtained from a combined microcalorimetric and IR-spectroscopic study. Such types of data were also obtained for Na- and K-ion-exchanged ZSM-5 samples. Furthermore, a linear relationship between the differential heat of adsorption (qdiff) evaluated and the shift of wavenumber of the C–O stretching vibration from that of a gaseous CO molecule (Δν) was established for the systems of MZSM-5–CO, and the bonding nature of the CO molecule with each site can be explained in terms of the electrostatic force. The model of each adsorption site was also examined by the quantum calculation method (density functional theory: DFT). The trends obtained from the experimental data may be substantially supported by the calculation method even adopting a model as simple as the ZSM-5-type zeolite: the composition of MAlSi4O4H12.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...