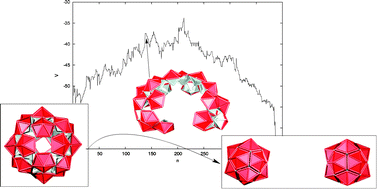
Energy landscapes for shells assembled from pentagonal and hexagonal pyramids
Abstract
We present new rigid body potentials that should favour efficient
- This article is part of the themed collection: Coarse-grained modeling of soft condensed matter

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...