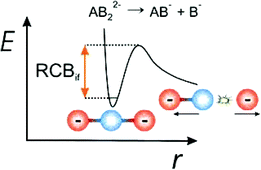
Multiply charged anions (MCAs) represent exotic, highly energetic species in the gas-phase due to their propensity to undergo unimolecular decay via electron loss or ionic fragmentation. There is considerable fundamental interest in these systems since they display novel potential energy surfaces that are characterized by Coulomb barriers. Over recent years, considerable progress has been made in understanding the factors that affect the stability, decay pathways and reactivity of gas-phase MCAs, mainly as a result of the application of electrospray ionization as a generic technique for transferring solution-phase MCAs into the gas-phase for detailed characterization. We review contemporary work in this field, focusing on the factors that control the intrinsic stability of MCAs, both as isolated gas-phase ions, and on their complexation with solvent molecules and counter-ions. While studies of MCAs are primarily of fundamental interest, several classes of important biological ions are commonly observed as MCAs in the gas-phase (e.g. oligonucleotides, sugars). Recent results for biologically relevant ions are emphasised, since a fundamental understanding of the properties of gas-phase MCAs will be highly valuable for developing further analytical methods to study these important systems.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...