Quantification of ion-induced molecular fragmentation of isolated 2-deoxy-d-ribose molecules†
Abstract
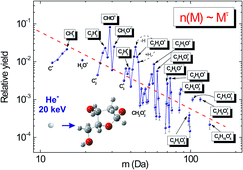
Recent experiments on low energy ion-induced damage to DNA building blocks indicate that ion induced DNA damage is dominated by deoxyribose disintegration (Phys. Rev. Lett., 2005, 95, 153201). We have studied interactions of keV H+ and Heq+ with isolated deoxyribose molecules by means of high resolution time-of-flight

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...