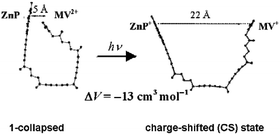
Photophysical studies with semi-rigid, 1, and flexible, 2, donor–bridge–acceptor (D–b–A2+) molecules with D a porphyrin and A2+ a methyl viologen moiety, were performed in neat polar solvents as well as included in surfactant (DTAB) aqueous and in reverse AOT/n-alkane micelles. The micelles acted as nanoreactors for the photoinduced electron transfer reaction upon laser excitation. In spite of the longer lifetime of the charge separated (CS) state in the semi-rigid tetrad 1
(ca. 200 ns vs. ca. 100 ns for the flexible dyad 2), the CS formation quantum yield, for example in acetonitrile, was lower for the former (ΦCS
= 0.13) than for the latter (0.58). Comparison of the time-resolved fluorescence data in neat solvent and in the micelles yielded the ΦCS values in the dilute micellar solutions. Application of laser-induced optoacoustic spectroscopy at various temperatures to 1 dissolved in a polar organic solvent (benzonitrile, BZN) included in aqueous DTAB nanoreactors afforded structural volume changes for the production in hundreds of ps of the CS state upon excitation of a polar molecule. The contraction during CS formation upon excitation of the collapsed conformer in BZN is attributed to the entering of solvent into the open molecular cavity. The opening upon formation of the CS state due to photoinduced electron transfer in the 1 collapsed conformation arises from the repulsion of the two positively charged ends in this state, as previously calculated. Inclusion of 1 in reverse AOT micelles in various n-alkanes also led to a contraction upon excitation, but the data had much more error due to the limited range of variability of the ratio of thermoelastic parameters. The data obtained with the more flexible “supermolecule”
2 showed the predicted large conformation flexibility of these molecules.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...