Low energy electron driven reactions in single formic acid molecules (HCOOH) and their homogeneous clusters
Abstract
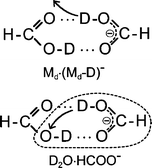
Low energy (0–3 eV) electron attachment to single formic acid (FA) and FA clusters is studied in crossed electron/molecular beam experiments. Single FA molecules undergo hydrogen abstraction via dissociative electron attachment (DEA) thereby forming HCOO− within a low energy resonance peaking at 1.25 eV. Experiments on the isotopomers HCOOD and DCOOH demonstrate that H/D abstraction occurs at the O–H/O–D site. In clusters, electron attachment is strongly enhanced leading to a variety of negatively charged complexes with the dimer M2− (M ≡ HCOOH) and its dehydrogenated form M·(M–H)− as the most abundant ones. Apart from the homologous series containing the non-dissociated (Mn−) and dehydrogenated complexes (Mn−1·(M–H)−, n ≥ 1) further products are observed indicating that electron attachment at sub-excitation energies (≈1 eV) can trigger a variety of chemical reactions. Among these we detect the complex H2O·(M–H)− which is interpreted to arise from a reaction initiated in the cyclic hydrogen bonded dimer target. In competition to hydrogen abstraction yielding the dehydrogenated complex M·(M–H)− the abstracted hydrogen atom can react with the opposite FA molecule forming H2O and HCO with the polar water molecule attached to the closed shell HCOO− ion. The FA dimer can thus be used as a model system to study the response of a hydrogen bridge towards dehydrogenation in DEA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...