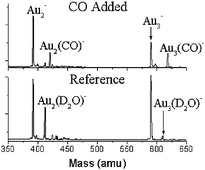
In the absence of moisture and at room temperature, the activity and saturation of CO on gold cluster anions, AuN−, are known to be highly dependent on the size of the cluster. Small AuN− clusters (N
= 2,3) showed no adsorption activity, and the saturation CO adsorption values did not increase proportionately to cluster size or area. Here, we report on the effects of water vapor and temperature on the ability of AuN− clusters to adsorb CO in a high-pressure, fast-flow reactor. In contrast to all earlier reports, our results using this method show that smaller gold-cluster anions bind single and multiple CO groups at ambient temperature and above. In particular, species previously unseen at room temperature, corresponding to Au2(CO)−, Au3(CO)− and Au4(CO)2−, have been observed. Apparently, the presence of water vapor facilitates the adsorption of CO on the smaller clusters, possibly by aiding in the release of adsorption energy. As the number of studies concerning gold catalysis has continually increased over the past decade, these results provide important new information on the possible role of moisture in gold catalysis.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...