A novel CdII-based metal–organic framework as a multi-responsive luminescent sensor for Fe3+, MnO4−, Cr2O72−, salicylaldehyde and ethylenediamine detection with high selectivity and sensitivity†
Abstract
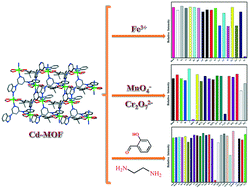
A novel luminescent CdII-based metal–organic framework {[Cd(BBIP)(TBIP)]·EtOH}n (1) derived from the multidentate 5-tert-butylisophthalic acid (H2TBIP) and the semi-rigid N-donor 3,5-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)pyridine (BBIP) has been solvothermally synthesized and structurally characterized by using infrared spectroscopy, thermal analysis, single-crystal X-ray diffraction and powder X-ray diffraction. The adjacent CdII ions are linked by two carboxylate groups of one TBIP2− ligand with chelating mode to form a one-dimensional CdII-TBIP2− chain, which is further connected by the BBIP ligand to obtain a two-dimensional network. Interestingly, the fluorescence experiments indicate that 1 could be considered as a good multi-responsive sensing material for detecting Fe3+, MnO4−, Cr2O72−, salicylaldehyde (SA) and ethylenediamine (EDA) via the turn-off effect, with the detection limits of 0.53, 0.98, 3.6, 0.42 and 5.3 ppm, respectively. The luminescence quenching effect induced by Fe3+ could be mainly ascribed to the competitive absorption mechanism. The electron-transfer transition and competitive absorption mechanism could be used to explain the luminescence quenching of MnO4− and Cr2O72−. The turn-off effect of 1 on SA could be ascribed to the photoinduced electron-transfer and competitive absorption mechanisms. Meanwhile, the possible mechanism of fluorescence quenching caused by EDA could be attributed to the structure collapse. More importantly, 1 could be regenerated and reused after five cycles for Fe3+, MnO4−, Cr2O72− and SA detection. In a nutshell, 1 could be employed as a multi-responsive luminescent sensor used for the highly selective and sensitive detection of metal ions, anions and small organic molecules.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Coordination Networks


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...