Multifunctional fluorescence responses of phenyl-amide-bridged d10 coordination polymers structurally regulated by dicarboxylates and metal ions†
Abstract
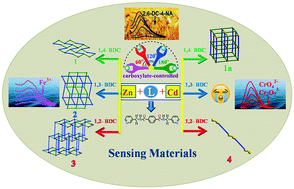
To investigate the effects of metal ions and angles of the carboxyl groups of dicarboxylates on the structures of coordination polymers, four Zn(II)/Cd(II) coordination polymers [Zn(L)(1,4-BDC)]·H2O (1), [Zn(L)(1,3-BDC)]·H2O (2), [Zn(L)(1,2-BDC)] (3) and [Cd(L)0.5(1,2-BDC)(H2O)] (4) [L = N,N′-bis(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-terephthalamide, 1,4-H2BDC = terephthalic acid, 1,3-H2BDC = isophthalic acid, 1,2-H2BDC = phthalate] were prepared under hydrothermal conditions. Polymers 1 and 2 are 2D structures with 63 and 44 topology. Polymer 3 shows a 4-connected 3D framework, and 4 features a 1D structure with single/double alternate linkers. The effects of the positions of carboxyl groups and the coordination characteristics of metal ions on the structures of the title coordination polymers were studied. The title coordination polymers show multi-functional fluorescence responses towards metal ions (Fe3+), anions (CrO42−, Cr2O72−) and pesticides (2,6-DC-4-NA) and good stability in a wide range of pH values. Taking 1 as an example, the mechanism was also explored by UV-visible absorption spectroscopy and the fluorescence lifetime experiment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...