Hollow single-crystalline octahedra of hydrated/dehydrated hydroxyl ferric phosphate and crystal-water-enhanced electrochemical properties of the hydrated sample for reversible lithiation–delithiation†
Abstract
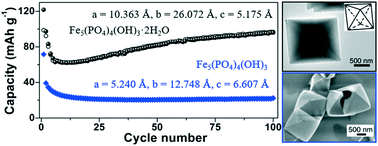
The solution-based preparation of a polyanionic inorganic compound sometimes introduces structural water into its chemical composition; however, to date, the positive impact of this structural water on the electrochemical properties of the hydrated sample is still ambiguous. Herein, hollow single-crystalline octahedra of hydrated hydroxyl ferric phosphate (Fe5(PO4)4(OH)3·2H2O; edge length: ∼1.0 μm; a known orthorhombic phase) and its dehydrated counterpart (Fe5(PO4)4(OH)3; edge length: ∼0.9 μm; a fitting orthorhombic phase) were uniformly prepared for the first time, facilitating comparative studies on their structural and electrochemical properties. As a lithium-ion battery cathode within 1.5–4.5 V vs. Li+/Li, the hydrated sample can deliver the initial discharge capacity of 176.6 mA h g−1 at 5 mA g−1, which is close to the theoretical value of 180.0 mA h g−1. By comparison, regardless of the charge–discharge current rate, the reversible capacity of the hydrated microcrystallites in each cycle was much higher than that of the dehydrated counterparts. In other words, the 1,2-propanediol solvent mainly determines the hydro-/solvothermal formation of Fe5(PO4)4(OH)3·2H2O hollow single-crystalline octahedra, and it is the presence of crystal water that modifies the cell parameters of the orthorhombic lattice and promotes the reversible lithiation–delithiation capability of microcrystallites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...