Origins of optical defects in rapidly grown DKDP crystals†
Abstract
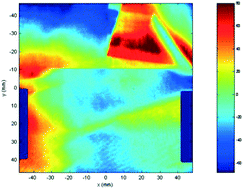
DKDP crystals were rapidly grown by a novel method under stationary conditions. The optical homogeneity of slabs cut from them was investigated. Wavefront distortions were found to be located in a specific growth sub-sector and several contributing sources were identified: point structural defects in the bulk, inhomogeneous surface losses of deuterium and surface planarity. A correlation has been established between all the sources explaining their joint localization and the relationship between optical inhomogeneity and crazing. The relative importance of each contribution was evaluated leading to an estimated bulk refractive index inhomogeneity of a few 10−6 to 1.10−5 for these DKDP crystals, which is similar to those previously observed for KDP rapidly grown by the polythermal method.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...