Crystallisation and physicochemical property characterisation of conformationally-locked co-crystals of fenamic acid derivatives†
Abstract
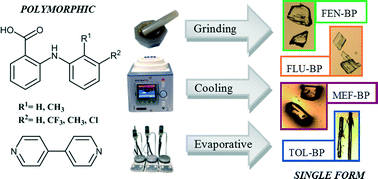
Polymorphism in drug compounds can cause significant problems for industrial-scale production and so a method for restricting the conformational freedom of the target compound whilst retaining desired chemical properties is highly beneficial to the pharmaceutical industry. Co-crystallisation is commonly used to alter the structure of an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) without affecting its activity. A comprehensive co-crystal screen of four fenamic acid derivatives affords a strictly limited number of co-crystals. These show no evidence of polymorphism, although some of the parent APIs exhibit significant polymorphism. Two of these co-crystals, of mefenamic acid and tolfenamic acid with 4,4′-bipyridine, were previously unknown and are studied using X-ray diffraction. Co-crystals from this screen are fully characterised and display comparable solubility and stability with respect to the parent APIs; no phase transformations have been identified. A range of crystallisation techniques, including cooling and grinding methods, are shown to afford single polymorphic forms for each of the co-crystals.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...