Lanthanide contraction effects on the structures, thermostabilities, and CO2 adsorption and separation behaviors of isostructural lanthanide–organic frameworks†
Abstract
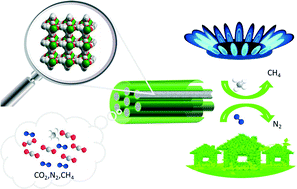
A systematic investigation of the CO2 adsorption and separation behaviours of fourteen isostructural lanthanide–organic frameworks (LOFs) of lanthanide benzenetricarboxylate (LnBTC) is executed, where Ln = Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm and Yb. These LOFs are facilely synthesized and randomly scaled by heating a mixture of 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid and lanthanide nitrate solution with reaction time less than 1 h. Structure refinement reveals that these LOFs exhibit three-dimensional networks with one-dimensional channels and open metal sites on the pore walls. Thermogravimetric analyses verify that these LOFs are stable up to 540 °C. Influenced by the opposing effects of ionic radius and molecular mass from Y(III)–Yb(III), the LOFs with the highest CO2 uptakes are YBTC at 273 K and PrBTC at 298 K at atmospheric pressure. Moreover, the real CO2 separation from binary gas mixtures of CO2–N2 and CO2–CH4 further indicates that the lanthanide contraction plays the most important role in tuning the adsorption and separation performance of the resulting materials. This work may give rise to the potential application of highly thermostable porous LOF materials in carbon dioxide capture from flue gas and natural gas, in order to reduce greenhouse emissions and improve energy efficiency.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...