Rare-earth doped LaF3 hollow hexagonal nanoplates: hydrothermal synthesis and photoluminescence properties
Abstract
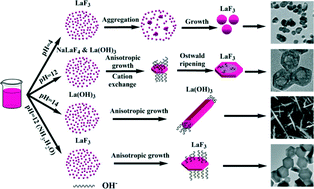
A facile hydrothermal route at designated pH values has been developed to synthesize a series of well-dispersed LaF3 colloidal nanocrystals (NCs) with a rich variety of morphologies, including nanoparticles, hexagonal nanoplates and fullerene-like nanoparticles. X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and photoluminescence spectroscopy were used to characterize the samples. It is found that the formation of monodispersed fluoride NCs not only closely correlates with the pH values of the mother solutions, but also depends on the basicity of the base employed to adjust the pH value. The strong alkaline solution in the absence of any organic additive in this system was found to be a prerequisite for producing hexagonal fullerene-like LaF3 nanodisks. A mechanism for the formation of the fullerene-like LaF3via the local Ostwald ripening process has been proposed based on observations of time-dependent experiments. The multicolor upconversion (UC) emission was successfully realized in a series of Yb3+/Er3+ doped LaF3 NCs by excitation in the near-infrared region. The UC emission ratios of red to green for a series of LaF3 NCs can be tuned by adjusting the pH values of the mother liquids, and an UC mechanism activated by high-energy phonons inherent in the hollow LaF3 nanoplates is proposed. It is expected that these rare-earth fluoride NCs might have potential applications in photocatalysis, biolabelling and drug-delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...