Mechanochemical synthesis and characterisation of two new bismuth metal organic frameworks†
Abstract
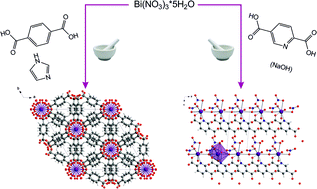
Two metal organic structures composed of the ligands benzene-1,4-dicarboxylate and pyridine-2,5-dicarboxylate and bismuth cations are presented: (H2Im)[Bi(1,4-bdc)2] (1) and [Bi(pydc)(NO3)2(H2O)2]·H2O (2) (bdc = benzenedicarboxylate, H2Im = imidazole cation, pydc = pyridinedicarboxylate). Both compounds were synthesised via grinding and the crystal structure of compound (2) was solved based on its powder diffraction pattern. Compound 1 crystallised isostructurally to the dimethyl ammonium containing compound (dma)[Bi(1,4-bdc)2]. Raman spectroscopy and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) measurements provided additional information about the two mechanochemically synthesised metal organic compounds.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...